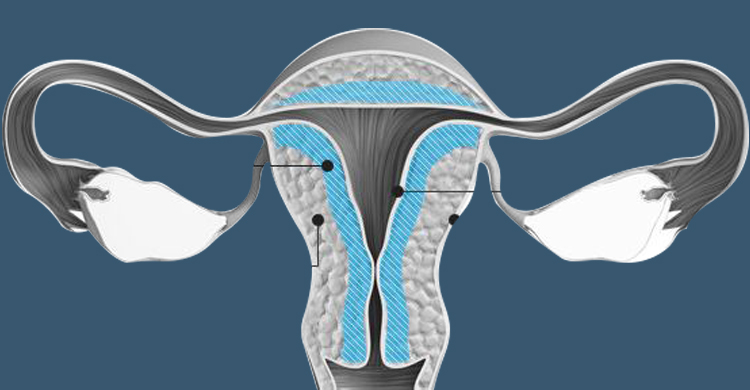
Adenomyosis is a disorder of the female reproductive system in which the endometrium, the uterus' inner lining, breaches the muscle wall (the myometrium). This additional tissue might result in the uterus growing by two or three times its original size, which can cause irregular uterine flow and uncomfortable periods.
Adenomyosis can occasionally go undetected or cause little pain. Yet adenomyosis can result in:
Prolonged or heavy menstrual bleeding
During menstruation, severe cramping or acute, knife-like pelvic pain (dysmenorrhea).
Persistent pelvic discomfort
Painful sex (dyspareunia).
Your uterus may enlarge. Even though you might not know whether your uterus has grown, you might feel pressure or soreness in your lower abdomen.
The exact cause of adenomyosis is still unknown to the experts.
Pelvic exam: During a pelvic exam, your doctor can discover that your uterus has grown bigger, gotten softer, or become more painful to touch.
Ultrasound: Sound waves are used to capture pictures of the pelvic organs during a transvaginal ultrasound. These pictures often reveal thickening of the muscle, which raises the possibility of adenomyosis.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): MRI scans of the uterus can reveal uterine enlargement and thickness in certain regions, which may be signs of adenomyosis.
Biopsy: Since tissue develops inside the uterine walls, tissue can only be sampled following hysterectomy, which eliminates the uterus.
Adenomyosis symptoms frequently disappear after menopause because estrogen, a female hormone, encourages the formation of endometrial tissue. In the meantime, these therapies can reduce discomfort, significant bleeding, and other symptoms:
Pain relievers: Anti-inflammatory medicines such as ibuprofen or naproxen are used to treat pain.
Hormonal therapy: Estrogen can worsen bleeding and cramps by thickening the uterine wall. Several hormonal contraceptives can stop menstruation and its symptoms.
Hysterectomy: In this treatment method, the uterus is removed. You won't have a menstrual cycle or be able to become pregnant after a hysterectomy.