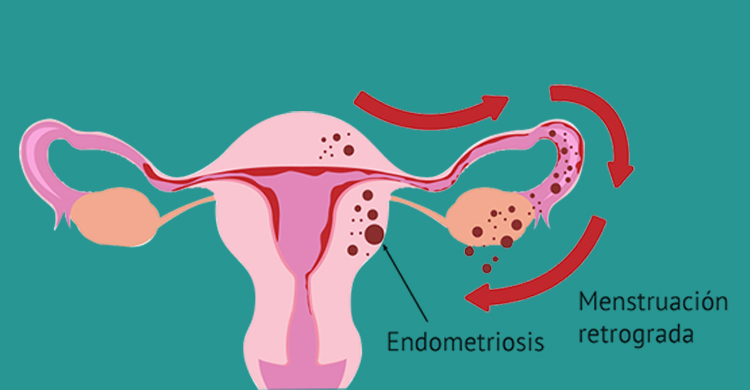
Endometriosis is a condition in which tissue that normally grows inside the uterus grows outside of it. This can cause pain, irregular bleeding, and other symptoms. It can also affect fertility. Treatment for endometriosis may include medication or surgery, depending on the severity of the condition.
The most common symptoms of endometriosis are pelvic pain and cramping, especially during menstrual periods. Other symptoms may include pain during sex, heavy or irregular periods, and pain with bowel movements or urination. Some women with endometriosis may also experience difficulty getting pregnant.
It's important to talk to a doctor if you are experiencing any of these symptoms, as they can be caused by other conditions as well. A doctor can determine the cause of your symptoms and recommend appropriate treatment.
There is no sure way to prevent endometriosis, as the exact cause of the condition is not known. However, there are some things that may help reduce your risk of developing the condition or help manage its symptoms. These include:
Managing stress : Chronic stress can worsen the symptoms of endometriosis, so finding ways to manage stress, such as through exercise, meditation, or therapy, may be helpful.
Eating a healthy diet : A diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help support overall health and may help manage the symptoms of endometriosis.
Avoiding exposure to environmental toxins : Some chemicals and pesticides may act as endocrine disruptors, which can interfere with hormone levels and potentially increase the risk of endometriosis. Avoiding exposure to these substances, when possible, may help reduce your risk of developing the condition.
Using barrier methods of contraception: Hormonal birth control, such as the pill or the patch, can help manage the symptoms of endometriosis by regulating hormones and reducing menstrual bleeding. However, some forms of hormonal birth control, such as the intrauterine device (IUD), can increase the risk of endometriosis. If you are at risk of the condition or have been diagnosed with it, your doctor may recommend using a barrier method of contraception, such as condoms, instead.
but some studies have suggested that certain dietary changes may help manage the symptoms of the condition. These include:
Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains: A healthy, balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help support overall health and may help manage the symptoms of endometriosis.
Avoiding processed foods and added sugars: Processed foods and foods high in added sugars may contain chemicals and additives that can act as endocrine disruptors and potentially worsen the symptoms of endometriosis. Avoiding these foods, when possible, may help reduce your symptoms.
Limiting caffeine and alcohol: Caffeine and alcohol can both affect hormone levels and worsen the symptoms of endometriosis. Limiting your intake of caffeine and alcohol, or avoiding them altogether, may help reduce your symptoms.
Incorporating omega-3 fatty acids into your diet: Some studies have suggested that omega-3 fatty acids, which are found in fatty fish and plant-based oils, may help reduce inflammation and manage the symptoms of endometriosis.
It's important to remember that every person is different, and what works for one person may not work for another. It's best to work with a healthcare provider to develop a plan that is right for you.
Treatment for endometriosis will depend on the severity of the condition and the symptoms a person is experiencing. Mild cases of endometriosis may not require treatment, but more severe cases may be treated with medication or surgery.
Hormonal birth control : Hormonal birth control, such as the pill or the patch, can help regulate hormones and reduce the growth of endometrial tissue.
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists : These medications can help reduce the levels of estrogen in the body, which can slow the growth of endometrial tissue.
Aromatase inhibitors : These medications can block the production of estrogen in the body, which can help reduce the growth of endometrial tissue.
The type of surgery performed will depend on the location and size of the endometrial tissue. Options may include:
Hormonal birth control : Hormonal birth control, such as the pill or the patch, can help regulate hormones and reduce the growth of endometrial tissue.
Laparotomy : This is a more invasive surgery in which a larger incision is made in the abdomen to remove endometrial tissue.
Hysterectomy : In severe cases, a hysterectomy, or the removal of the uterus, may be recommended. This is a major surgery and is usually only considered as a last resort.