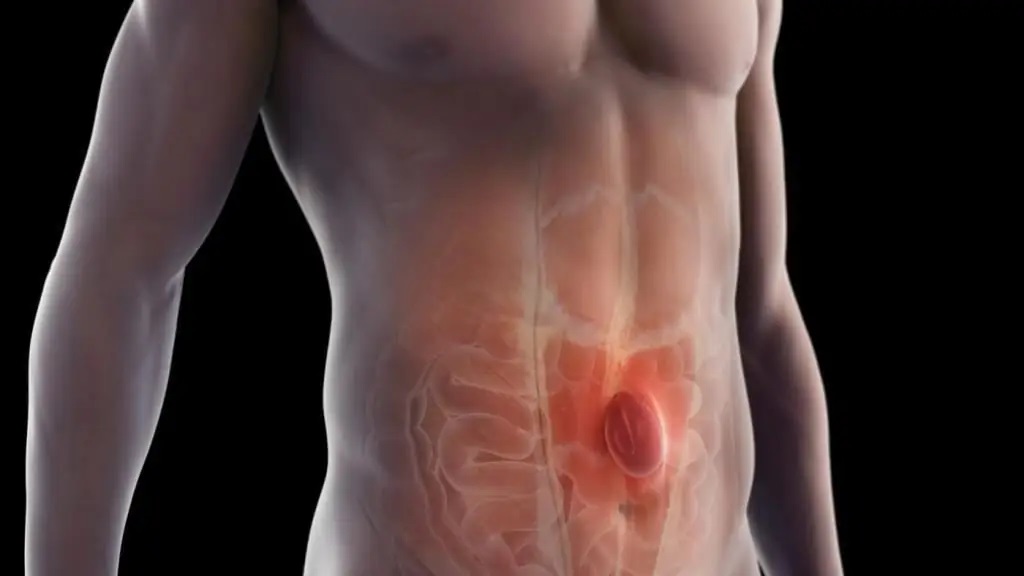
When an internal organ or other body parts pushes through the muscle or tissue surrounding it normally, it becomes a hernia. Most hernias develop in the abdomen, between the chest and the hips.
When tissue, such as a section of the intestine, pushes through a weak area in the abdominal muscles, it develops into an inguinal hernia. The ensuing bulge may hurt when you cough, lean over or lift anything heavy. It is mainly seen in males.
This type of hernia is formed when fatty tissue or a part of the intestine bulges or protrudes into the groin area. Femoral hernias, which mostly afflict older women, are far less prevalent than inguinal hernias.
Near the navel or belly button, fatty tissue or a portion of the intestine protrudes through the abdomen.
This hernia develops when a section of the stomach protrudes into the chest cavity through a gap or opening in the diaphragm.
Inguinal and femoral hernias are brought on by weak muscles, which may have existed from birth, or by age and constant stress on the groin and abdominal regions. Such strain might result from strenuous physical activity, obesity, pregnancy, persistent coughing, or constipation-related toilet strain.
Adults who strain their abdomen region, are overweight, have a persistent, heavy cough, or have just given birth may develop an umbilical hernia. Smoking, a family history of hernia, cystic fibrosis, low birth weight, etc., are also factors that increase the risk of developing a hernia.
The primary symptoms of a hernia are:
The symptoms of a hernia can be reduced with exercises to strengthen the muscles surrounding the affected region. Exercises to reduce weight might also help you ease the symptoms.
Surgery may be the sole option to treat hernias because they frequently do not get better independently. The best treatment for your hernia will be suggested by your doctor, who may also refer you to a surgeon.
If the surgeon determines that fixing your hernia is required, they will choose the best procedure that suits your requirements. Hernia can be fixed by either open surgery or laparoscopic surgery.